Our Group organises 3000+ Global Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ ������ý Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
������ý Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
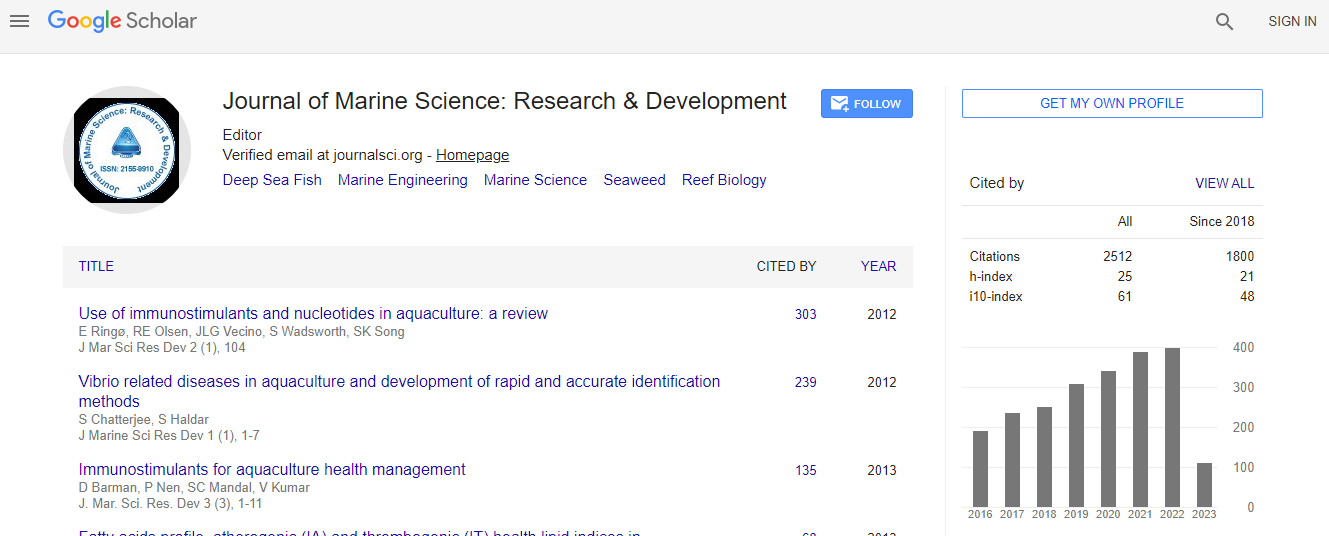
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- ������ý J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Macro-epifaunal community dynamics in a tropical estuary: Effects of salinity and acidification
2nd International Conference on Oceanography
M Belal Hossain and David J Marshall
Accepted Abstracts: J Marine Sci Res Dev
DOI: