Our Group organises 3000+ Global Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ ������ý Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
������ý Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
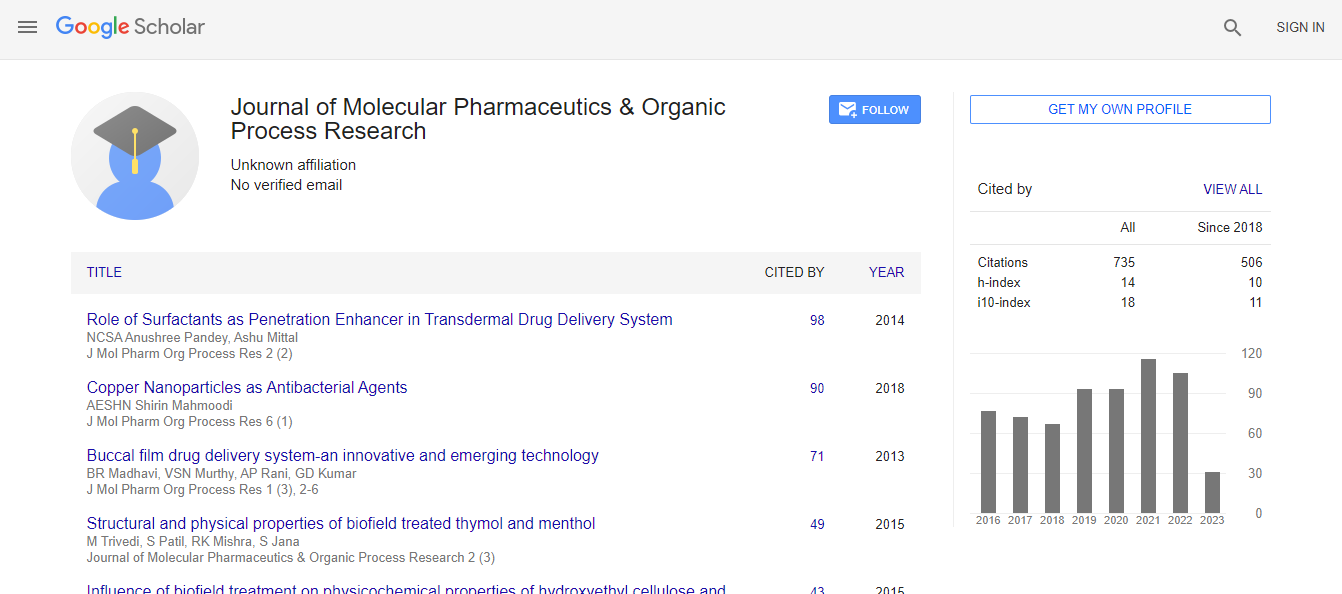
Citations : 1057
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- ������ý J Gate
- Academic Keys
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Share This Page
Probiotic potentiality and antibacterial activity of honey derived Lactobacillus plantarum from Malda, India
2nd International Conference on Pharmaceutical Formulations and API
Surajit Roy and Shyamapada Mandal*
University of Gour Banga, India
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Mol Parm Org Process Res
Abstract
Background: The beneficiary role of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) as potential probiotics is well accepted worldwide. The objective of our current study was to isolate and identify LAB from natural honey as well as to investigate the probiotic potentiality and antibacterial activity of the isolates. Methods: Freshly collected natural honeys were streaked on MRS agar plate and incubated at 37�?�?�?°C for 24-48 hrs. The isolated single bacterial colony was then subcultured to obtain pure colony. The LAB isolates were identified performing both conventional as well as molecular identification by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phylogenetic tree analysis. Probiotic potentiality of isolated LAB was tested against a number of parameters. Broad spectrum antibacterial activity of the LAB was performed by both agar-overlay and agar-well diffusion methods. The results obtained in terms of ZDI (in mm) were interpreted accordingly. Results: Two LAB strains (LMEMh and LMEMh1) were isolated from honey samples (mustard and multifloral) and were identified as Lactobacillus plantarum. Both the strains were tolerant to low pH, high concentration of sodium chloride and bile salt. In agar-overlay method, the lactobacilli showed broad spectrum antibacterial activity with ZDI (Zone Diameter of Inhibition) values ranged from 13.67 �?�?�?± 0.47 mm to 31.67 �?�?�?± 0.94 mm. Following agar well diffusion, ZDI values of culture filtrate (at pH 5.5) were ranged from 10.33 �?�?�?± 1.25 mm to 20.33 �?�?�?± 1.70 mm whereas no zone of inhibition was observed for the culture filtrate, at pH 7.0, against pathogenic bacterial strains. Conclusion: LAB isolates possess excellent antibacterial activity and are useful agent with probiotic potentiality. Keywords: Lactic acid bacteria, Probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum, Zone diameter of inhibition.Biography
Shyamapada Mandal is Professor and Head of the Department of Zoology and Dean (Science), University of Gour Banga, India. He is interested on infectious diseases, probiotics and genomics and bioinformatics research. He did pre-PhD, PhD and post-PhD research under the guidance of Professor Nishith Kumar Pal at Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine, India. He has published 118 articles with eight book chapters. He is life member of IAMM and IASR, India and fellow member of SASS, India. Eight national academic and research awards have been conferred to him. He has guided 52 post graduate students; supervised three MPhil and three PhD students and supervising 6 PhD and one MPhil students. He is among the world’s top 2% scientists as per the survey of the Stanford University, published in PLOS (Public Library of Science) Biology (October, 2020). He is featured in the top 2% world scientists list for second consecutive time as published by the Stanford University-Elsevier BV (October, 2021).